Atrial Fibrillation
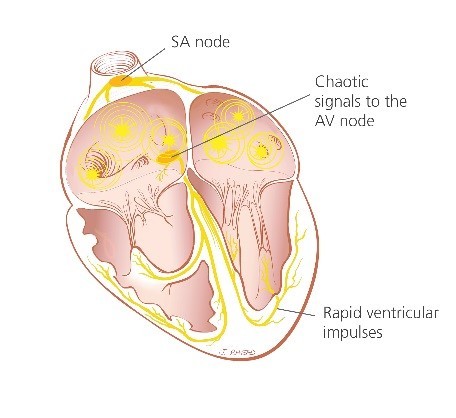
Atrial fibrillation is an irregular heart rhythm that affects the upper chambers (atria) of the heart.
Atrial fibrillation is an irregular heart rhythm that affects the upper chambers (atria) of the heart.
This abnormal, irregular heart rhythm is also referred to as an arrhythmia which can affect the efficiency of blood flow to the rest of the body.
Atrial fibrillation is categorized in 3 forms:
- Paroxysmal (intermittent/ sporadic episodes)
- Persistent (episodes lasting longer than a week or requiring treatment to terminate)
- Permanent
The type of atrial fibrillation you have will help determine your treatment.
Treating atrial fibrillation is important because it increases your risk of stroke, heart failure and can impact negatively on your quality of life.
Causes:
The cause of atrial fibrillation is often unclear, however the following factors are known to increase the risk:
- Hypertension
- Ischemic heart disease
- Excess weight
- Smoking
- Caffeine
- Excessive Alcohol use
- Sleep apnea
- Thyroid dysfunction
Common Symptoms
The symptoms often reported by patients but not limited to include:
- Palpitations (fast, irregular thumping of the heart)
- Chest discomfort or pain
- Breathlessness
- Fatigue or malaise
Diagnosis:
Detection and recording of atrial fibrillation can often be challenging. The following tests might be used to determine whether you have atrial fibrillation:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Echocardiogram to detect possible structural defects and overall function of the heart
- Monitoring devices such as a Holter, Event recorder or LINQ (implantable loop recorder)
- Blood tests to assess reversible causes eg/ electrolyte imbalances, thyroid disease.
Treating Atrial Fibrillation
Goals of treatment include:
- Controlling the heart rate hereby allowing the ventricles (lower chambers) to fill adequately.
- Restoration of sinus rhythm (normal regular heart rate) allowing the atria and ventricles to work together more efficiently.
- Symptom management to improve quality of life
- Reduction of stroke risk
Treatment Options:
- Medication to control the heart rate and or rhythm
- Blood thinners (anticoagulation) to reduce the risk of stroke
- Cardioversion under sedation to restore the normal heart rhythm (sinus rhythm)
- Catheter ablation to terminate abnormal electrical pathways in the heart
- Intra-cardiac devices (pacemaker or defibrillator) to detect and terminate onset of atrial fibrillation.
Talk to your doctor to determine which treatment option best suits you.
References: